Pneumothorax
What is Pneumothorax?
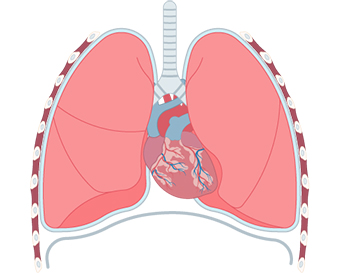
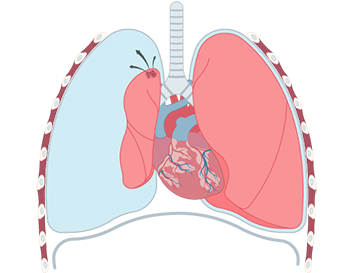
A disease in which there is a hole in the lung and air fills the pleural cavity
It is a disease in which there is a hole in the thin membrane surrounding the lungs, causing air to fill in the chest cavity, constricting the lungs, and reducing lung capacity. It is divided into ‘spontaneous pneumothorax’, which occurs in people with no specific cause or existing lung disease, and ‘traumatic pneumothorax’, which occurs due to external shock. Pneumothorax is a disease with a high recurrence rate of more than 40%, and continuous observation is required if there is a history.
Causes and Symptoms
-
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax : It occurs when the inhaled air leaks into the pleural cavity through a hole formed by the bursting of alveolar vesicles on the surface of the lungs.
- Primary spontaneous pneumothorax : It mainly occurs in the younger age group and is caused by smoking, frequent chest compressions, lack of nutrition, and lungs not keeping up with the body's growth rate.
- Secondary Pneumothorax : It mainly occurs in the elderly and is caused by lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, tuberculosis, asthma, or genetic influences.
- Menstrual pneumothorax : Pneumothorax accompanied by dyspnea and chest pain within 72 hours before and after menstruation occurs in connection with menstruation.
- Ultraviolet pneumothorax : It occurs when air enters the pleural cavity as a result of an external shock, such as a car accident or fall.
-
Sudden chest pain and shortness of breath
- 1.Sharp stabbing chest pain
- 2.Uncomfortable breathing and a feeling of tightness in the chest that gets worse
- 3.Dyspnea symptoms according to the degree of pneumothorax
How to diagnose?
| [Medical Questionnaire and Medical Examination] |
A thoracic surgeon uses a stethoscope to identify diseases by breathing sound. |
| [Image Examination] |
A chest X-ray is used to check the pleural cavity and lungs. It is accompanied by a CT scan to determine the location of the alveolus that causes pneumothorax and to check for other lung diseases. |
How to treat?
The goal of fibromyalgia treatment is to detect the disease at an early stage to suppress symptoms and prevent organ damage.
-
Medication Treatment

Conservative treatment with oxygen therapy, etc.: Wait until the hole in the lung is healed.
-
Non-surgical Treatment
Chest tube intubation: A plastic tube is inserted into the chest cavity to drain air from the chest cavity.
Pleurodesis: The entire lung pleura and parietal pleura are attached using drugs to directly block air leaks in the lungs.
Thoracoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive incision removes the air sac to cure pneumothorax and to prevent recurrence.